Garage doors are essential components of many homes, providing security, convenience, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the various components of a garage door and how they work together can help homeowners maintain and repair their garage doors effectively. In this article, we will delve into the diagram of garage door parts, discuss their functions, and provide valuable maintenance tips to ensure your garage door operates smoothly.
Introduction to Garage Doors
A garage door is not just a functional entryway for vehicles; it also plays a vital role in your home’s overall security and energy efficiency. Typically made of metal, wood, or fiberglass, garage doors can come in various styles, including sectional, roll-up, and tilt-up. Regardless of the type, most garage doors share common parts that are crucial for their operation.
Common Types of Garage Doors
Before diving into the specifics of the diagram of garage door parts, it’s essential to understand the common types of garage doors:
- Sectional Garage Doors: These doors are made of several panels connected by hinges. They open vertically and are ideal for most homes due to their space-saving design.
- Roll-Up Garage Doors: Made from a single sheet of material, these doors roll up into a coil when opened. They are often used in commercial settings but can also be found in residential applications.
- Tilt-Up Garage Doors: These doors are constructed as a single piece and tilt up into the garage. They require more clearance space than sectional doors but are straightforward in design.
- Slide to the Side Garage Doors: These doors slide open to the side of the garage rather than rolling up or tilting. They are less common but can be an excellent choice for homes with limited headroom.
Read too: How To Replace Garage Door Roller Like a Pro? Step-by-Step Guide
The Diagram of Garage Door Parts
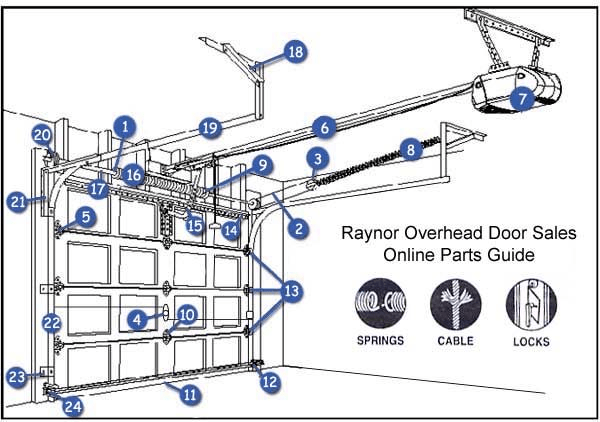
A typical garage door comprises various parts that work together to ensure its functionality. The diagram of garage door parts illustrates the relationship between these components, making it easier to understand how they function. Below is a description of each part included in the diagram:
1. Garage Door Panels
The garage door panels are the large, flat sections that make up the door itself. They can be made of different materials, including steel, wood, aluminum, or fiberglass. The number of panels can vary depending on the door’s design.
2. Tracks
Garage door tracks are the metal rails that guide the door as it opens and closes. They are usually mounted to the walls of the garage and help ensure smooth operation. Tracks can be horizontal or vertical, depending on the garage door’s design.
3. Rollers
Rollers are small wheels that fit into the tracks, allowing the garage door to move up and down smoothly. They come in various sizes and materials, such as plastic or steel, and should be lubricated regularly to prevent wear and tear.
4. Springs
Springs are essential components that counterbalance the weight of the garage door, making it easier to open and close. There are two main types of springs:
- Extension Springs: Located above the tracks, these springs stretch when the door is closed and contract when the door opens.
- Torsion Springs: Positioned above the closed door, these springs twist to lift the door. Torsion springs are generally more durable and provide better performance than extension springs.
5. Cables
Cables connect the garage door to the springs and help distribute the door’s weight. When the door opens or closes, the cables pull the door along the tracks and work in tandem with the springs to ensure smooth operation.
6. Garage Door Opener
The garage door opener is the motorized device that controls the opening and closing of the garage door. It is usually mounted to the ceiling and can be activated using a remote control, wall switch, or smartphone app. Openers can be chain-driven, belt-driven, or screw-driven, each with its pros and cons.
7. Safety Sensors
Safety sensors are crucial for preventing accidents. They are typically located near the bottom of the garage door tracks and detect obstacles in the door’s path. If something obstructs the door’s movement, the sensors will signal the opener to stop and reverse the door’s motion.
8. Weather Stripping
Weather stripping is applied along the bottom edge of the garage door and helps seal the gap between the door and the garage floor. It prevents drafts, moisture, and debris from entering the garage, improving energy efficiency.
9. Handles and Locking Mechanisms
Handles and locking mechanisms provide additional security for your garage door. Most garage doors have a handle on the inside for manual operation, while external locks can deter unauthorized access.
Diagram of Garage Door Parts Overview
Here’s a simple illustration to summarize the diagram of garage door parts:
luaCopy code -------------------------
| Garage Door |
|------------------------|
| Panel | Panel | Panel |
|------------------------|
| Rollers |
|------------------------|
| Tracks |
-------------------------
| Opener |
|------------------------|
| Safety Sensors |
-------------------------
| Weather Strip |
-------------------------
Maintaining Your Garage Door Parts
Regular maintenance of your garage door is essential to prolong its lifespan and ensure safe operation. Here are some maintenance tips for the components discussed:
1. Inspect and Lubricate Moving Parts
- Rollers: Inspect the rollers for wear and lubricate them with a silicone-based lubricant to ensure smooth operation.
- Tracks: Clean the tracks to remove debris and ensure the rollers can move freely. Lubricate the tracks sparingly to avoid attracting dirt.
2. Check Springs and Cables
- Springs: Inspect the springs for signs of wear, such as rust or stretching. If you notice any issues, consider calling a professional for replacement, as working with springs can be dangerous.
- Cables: Check cables for fraying or wear. If you see any signs of damage, replace them immediately to prevent accidents.
3. Test Safety Sensors
Regularly test the safety sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly. You can do this by placing an object in the door’s path to see if it reverses properly. If the door doesn’t respond as it should, clean the sensors and check their alignment.
4. Inspect the Garage Door Opener
- Remote and Wall Switch: Check the batteries in the remote and ensure the wall switch is functioning.
- Motor: Listen for unusual noises when operating the opener, which may indicate a problem. If the motor is noisy, it might require professional servicing.
5. Maintain Weather Stripping
Inspect the weather stripping regularly for tears or gaps. Replace any damaged weather stripping to ensure optimal insulation and prevent moisture infiltration.
6. Regular Professional Inspections
Consider scheduling professional garage door inspections at least once a year. A trained technician can identify potential issues and provide solutions before they become major problems.
Conclusion
Understanding the diagram of garage door parts and their functions is essential for any homeowner. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can better maintain your garage door and address any issues that may arise. Regular maintenance and inspections will not only enhance the performance and longevity of your garage door but also ensure the safety and security of your home.
With the right knowledge and care, your garage door can provide reliable service for many years to come.

Leave a Reply