Introduction
If you’ve ever wondered Does A Garage Door Opener Need A Dedicated Circuit, you’re not alone. Many homeowners face confusion when installing or upgrading their garage openers. Understanding proper electrical requirements ensures safe, reliable operation and prevents potential hazards.
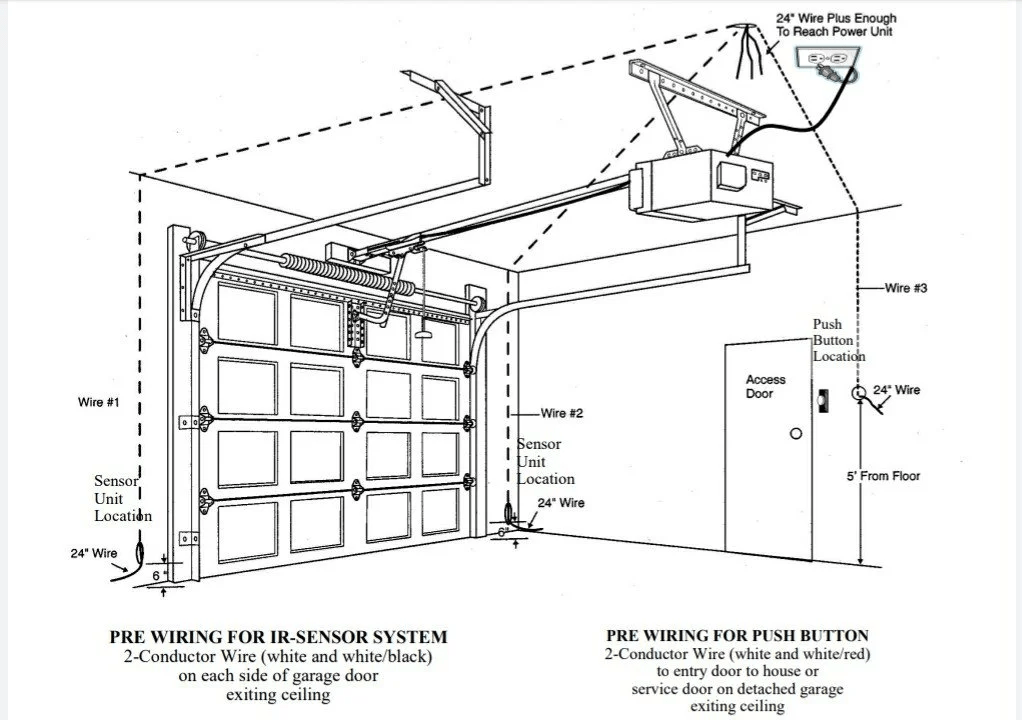
What Is a Dedicated Circuit and Why It Matters
A dedicated circuit is an electrical line reserved exclusively for a single appliance or device. In the case of garage door openers, this means the opener draws power directly from its own breaker without sharing the line with other devices.
Read too: How To Replace Garage Door Roller Like a Pro? Step-by-Step Guide
Key Benefits:
- Prevents overloads: Avoids tripping breakers due to multiple devices drawing power simultaneously.
- Improves reliability: Ensures the garage door opens consistently without electrical interference.
- Enhances safety: Reduces risk of fire or damage from overloaded circuits.
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), major motorized appliances, including garage door openers, often require a dedicated line to comply with safety standards. For more background, see Wikipedia.
Factors That Determine Circuit Needs
- Opener motor size
- Heavy-duty or commercial openers may draw more current, necessitating a dedicated circuit.
- Existing electrical load
- Sharing a line with high-draw devices like power tools or heaters increases the risk of tripping breakers.
- Frequency of use
- Openers used multiple times daily may benefit from dedicated power to maintain consistent performance.
- Local electrical codes
- Requirements may vary by region; always verify with a licensed electrician.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Dedicated Circuit
Step 1: Turn off main power
- Safety first: Switch off the main breaker before working on circuits.
Step 2: Choose the breaker
- Use a 15–20 amp breaker rated for motor loads, depending on your opener’s specifications.
Step 3: Run dedicated wiring
- Install a 14/2 or 12/2 gauge wire from the breaker panel to the garage opener location.
Step 4: Connect the outlet
- Mount a properly grounded outlet for the garage opener, ensuring it’s only powered by the dedicated line.
Step 5: Test the system
- Turn on the breaker and operate the garage door several times to verify stable operation.
Pro Tip: Label the breaker as “Garage Door Opener” to avoid accidental usage of the line by other devices.
Pros and Cons of a Dedicated Circuit
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Prevents breaker trips | Slightly higher installation cost |
| Improves opener reliability | May require professional electrician |
| Enhances safety | Takes additional space in breaker panel |
| Meets code requirements | Minor planning and wiring effort |
FAQ Section
Q1: Can I run my garage door opener on an existing outlet?
A1: While possible for small openers, it risks tripping breakers if other devices share the circuit.
Q2: What size breaker do I need for a standard garage door opener?
A2: Typically, a 15–20 amp breaker is recommended, but always check the opener’s manual.
Q3: Is it safe to DIY a dedicated circuit?
A3: Only if you have electrical experience; otherwise, hire a licensed electrician for safety and code compliance.
Q4: Does a dedicated circuit improve opener lifespan?
A4: Yes. Stable power reduces wear on the motor and electronic components.
Q5: Do all garages require dedicated circuits for openers?
A5: Not all, but it’s strongly recommended, especially for heavy-duty or frequently used openers.
Conclusion
Understanding Does A Garage Door Opener Need A Dedicated Circuit is crucial for safety, reliability, and long-term performance. Installing a dedicated circuit ensures consistent power, reduces breaker trips, and protects both your home and your garage opener. Share this guide with friends or family to help them safely optimize their garage door systems!


Leave a Reply