If you’re a homeowner dealing with a garage door repair or considering installing a new one, understanding the basic structure of a garage door is crucial. A garage door diagram can help visualize the different parts and their functions, providing insight into how each component contributes to the overall operation. While garage doors may seem straightforward, they consist of numerous interconnected parts, all of which work together to ensure smooth functioning.
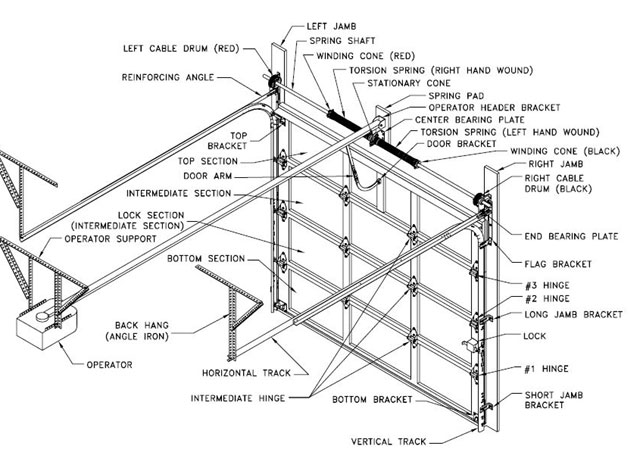
In this article, we’ll break down the most common elements seen in a garage door diagram, explain their roles, and discuss the importance of proper maintenance. Whether you’re trying to troubleshoot a problem or just want to understand your garage door better, this guide will give you a clearer understanding of how these essential components function.
What is a Garage Door Diagram?
A garage door diagram is a visual representation of the various parts and mechanisms that make up a garage door system. These diagrams are often used by homeowners, contractors, and repair professionals to identify and locate different components. Whether it’s a traditional, sectional, or rolling door, a garage door diagram illustrates the door panels, springs, tracks, cables, rollers, and other crucial parts.
Understanding these elements is essential for troubleshooting, repair, or routine maintenance. With a good grasp of a garage door diagram, you can save time, effort, and money when handling repairs or replacements.
Read too: The Complete Guide to Tighten Chain On Garage Door Opener for Smooth Operation
Key Components in a Garage Door Diagram
Before diving deeper into each part, let’s take a look at the primary components typically found in a garage door diagram:
- Door Panels
- Springs (Torsion or Extension)
- Tracks
- Cables
- Rollers
- Hinges
- Opener and Remote System
- Safety Sensors
- Weather Stripping
Now, let’s explore these components in detail.
Garage Door Diagram Breakdown: Key Components Explained
1. Door Panels
In any garage door diagram, the door panels are the most visible part of the door system. These panels make up the surface of the garage door and come in various materials such as steel, wood, aluminum, or fiberglass. A garage door can either be a single solid piece or segmented into multiple sections that fold up when the door is raised. Sectional doors are the most common in modern homes.
Why They’re Important:
The material and construction of the door panels contribute to the door’s durability, insulation, and appearance. It’s essential to select high-quality panels that meet your home’s aesthetic and functional needs.
2. Springs (Torsion and Extension Springs)
One of the most critical elements in any garage door diagram is the springs. They are responsible for balancing the weight of the door, making it easy to open and close manually or via a motorized opener.
- Torsion Springs: These are mounted above the garage door, and they twist (or torque) to lift the door as it opens. Torsion springs are generally safer and more durable than extension springs.
- Extension Springs: These springs stretch along the sides of the garage door tracks and extend when the door is closed. While more affordable, they require more space and maintenance.
Why They’re Important:
Springs store a large amount of energy, making them vital for smooth door operation. However, they can be dangerous if not properly maintained or installed, so understanding their role can prevent accidents or failures.
3. Tracks
The tracks are the metal rails on both sides of the garage door that guide it as it opens and closes. There are two sets of tracks: one vertical and one horizontal. The vertical tracks guide the door as it moves up and down, while the horizontal tracks hold the door in place when it’s fully open.
Why They’re Important:
Proper alignment of the tracks is crucial for smooth and safe door operation. Misaligned or damaged tracks can cause the door to get stuck or even come off its hinges, posing a safety risk.
4. Cables
Cables are often overlooked in a garage door diagram, but they play an essential role in the door’s functionality. Garage door cables are connected to the bottom of the door and are wound around drums at the end of the torsion spring system. They help lift and lower the door safely by distributing the tension from the springs.
Why They’re Important:
Cables wear down over time, and if they snap, they can lead to dangerous situations where the door could fall unexpectedly. Regular inspections are important to ensure their proper functioning.
5. Rollers
Rollers are small wheels that run along the tracks and help the garage door move smoothly when opening or closing. These rollers come in various materials, such as steel or nylon, and they are essential for reducing friction between the door and the tracks.
Why They’re Important:
Worn-out or damaged rollers can cause the garage door to operate noisily or unevenly. Replacing old rollers with high-quality nylon rollers can make your garage door quieter and smoother.
6. Hinges
Hinges connect the door panels and allow them to bend as the door opens and closes. In sectional garage doors, these hinges enable the panels to fold along the tracks, making it possible for the door to curve as it rolls up or down.
Why They’re Important:
Hinges are critical for ensuring that sectional doors fold and unfold smoothly without sticking. Over time, hinges can rust or become loose, leading to operational issues or even door misalignment.
7. Opener and Remote System
The garage door opener is the motorized device responsible for raising and lowering the garage door. Most openers are operated by a remote control, wall switch, or mobile app. The opener uses a trolley that moves along a rail to push or pull the door open or closed.
Why It’s Important:
Choosing a reliable garage door opener ensures smooth and convenient operation. Modern openers often come with added security features, such as rolling code technology, which changes the access code each time the door is operated to prevent unauthorized entry.
8. Safety Sensors
Modern garage doors include safety sensors located near the bottom of the door frame. These sensors use infrared beams to detect objects or people in the door’s path. If something interrupts the beam while the door is closing, the sensors will signal the door to stop and reverse its direction.
Why They’re Important:
Safety sensors are a mandatory feature in most residential garage doors, preventing accidents and injuries. Understanding their function can help you troubleshoot problems, such as when the door won’t close because of misaligned sensors.
9. Weather Stripping
Weather stripping is a crucial part of any garage door diagram that many homeowners overlook. It’s located at the bottom of the door and along the sides and top. Its primary purpose is to create a seal between the door and the garage frame to keep out dust, debris, and moisture.
Why It’s Important:
Good-quality weather stripping improves your garage’s energy efficiency by keeping out drafts and maintaining the desired temperature inside. It also helps prevent water damage and reduces noise pollution.
How to Read a Garage Door Diagram for Repairs
A garage door diagram is not just helpful for understanding the basic components of the door, but it’s also an invaluable tool when diagnosing and repairing problems. Whether you’re dealing with a broken spring, a noisy door, or a malfunctioning opener, using a diagram can help you quickly identify which part of the door needs attention.
Steps for Using a Garage Door Diagram for Repairs:
- Locate the Issue: Start by identifying the symptoms of the problem. Is the door not opening? Is it making unusual noises? Does it stop midway? Once you know the problem, you can refer to the diagram to locate the component that might be causing the issue.
- Check for Wear and Tear: Look at the moving parts in the diagram, such as springs, rollers, and cables. These parts experience the most stress and are usually the first to wear out.
- Understand Safety Measures: Springs and cables are under high tension, making them potentially dangerous to handle. The diagram can help you understand where these parts are located, allowing you to take appropriate safety precautions or decide if a professional is needed.
Maintenance Tips for Garage Door Components
Understanding the parts in a garage door diagram is just the first step. Regular maintenance of these components ensures smooth operation and extends the life of your garage door system.
1. Inspect and Lubricate Moving Parts
Apply a silicone-based lubricant to the springs, rollers, and tracks at least twice a year to keep everything moving smoothly. Avoid using grease, as it can attract dust and debris, leading to clogging.
2. Check Springs and Cables
Inspect the springs and cables for wear or fraying. If you notice any damage, contact a professional for repair or replacement. These parts are under high tension and can be hazardous if handled improperly.
3. Tighten Hardware
Over time, the vibrations from daily operation can loosen the hardware on your garage door, including hinges and bolts. Use a wrench to tighten loose parts and keep your door secure.
Conclusion
A garage door diagram provides an invaluable resource for homeowners who want to understand how their garage door functions. By familiarizing yourself with the different parts—such as door panels, springs, cables, and tracks—you can better maintain and troubleshoot your garage door. Regular upkeep and an understanding of the door’s components can prevent costly repairs and ensure that your garage door operates safely and efficiently.


Leave a Reply